Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Reflection of Light, Incident Ray, Average Speed of Image in Convex Mirror & Average Speed of Image in Concave Mirror etc.
Important Questions on Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
A luminous point object is placed at , whose images is formed at as shown in the figure. is the optical axis. Which of the following statements are correct?
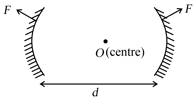
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, it is found that there is no gap between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of the convex mirror is:
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be:

The reflection surface of a plane mirror is vertical. A particle is projected in a vertical plane which is also perpendicular to the mirror. The initial velocity of the particle is 10 m/s and the angle of projection is 60o. The point of projection is at a distance 5 m from the mirror. The particle moves towards the mirror. Just before the particle touches the mirror the velocity of approach of the particle and its image is:
A plane mirror is placed along X-axis facing toward Y-axis. The one end of the mirror is at its origin. The equation of the image of an object is
If image of '' is formed at '' itself find values of ''.
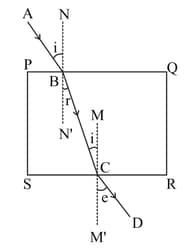
Observe the given figure and name the incident ray.
If the magnification produced by the mirror is , find the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror is
Which of the following points of a spherical mirror is taken as origin in case of measurement of concerning distance.
The first law of reflection states that:
A convex mirror used for rear-view on an automobile has a radius of curvature of . If a bus is located at from this mirror, What will be the position of image.
If angle of incidence, . Calculate the angle of reflection .
An object is placed in front of convex mirror whose radius of curvature is . Find the position and nature of image.
The object distance , image distance and focal length for a spherical mirror are related as
An object is placed at a distance from the convex mirror of focal length . The distance of image from the mirror is :
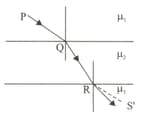
In the figure given below, PQRS denotes the path followed by a ray of light as it travels through three mediums in succession. The absolute refractive indices of the media are respectively. Then
A man run towards mirror at a speed of 5 m/s and the mirror fixed on the trolley which is moving away at a speed of 8 m/s. What is speed of his image?
A ray of light travels from A to B with uniform speed. On its way it is reflected by the surface. The path followed by ray to take least time is
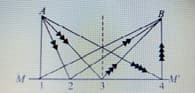
The focal plane of a spherical mirror:
Rays from sun converge at a point in front of concave mirror. Where should the object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
